 |
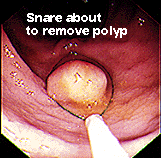
Early treatment for HNPCC patients is continuous
screening and quick removal of any polyps. The tissue of these polyps can
be tested to determine if they are cancerous or not. As shown, removal
of polyps is usually as simple, out-patient procedure. However, it is essential
for controlling the risk of cancer development.
Some people who have been identified as having the HNPCC mutation prefer to take drastic steps to reduce their chances of developing tumors. They may undergo surgery to remove the majority of the colon, and females will undergo a hysterectomy to have their uterus removed, along with removing their ovaries. These drastic procedures, however, do not completely eliminate their risks. |
Total abdominal hysterectomy and removal of both ovaries is recommended for women who are diagnosed with colon cancer and have already completed their families. (Ref. 7) Particularly with Lynch syndrome II, the female reproductive organs are at high risk of cancer development and they are very difficult to screen effectively. Removing these organs once cancer has been found is the best way to prevent future cancers from developing.
Newer techniques are hoping to make these aggressive
surgeries a rarity. For example, chemotherapy and the use of high dose
radiotherapy directly to the tumor during surgical procedures are being
studied as a means of reducing the extent of surgery. New chemotherapy
drugs are expected to help reduce recurrence. (Ref.
10)
Unfortunately, the progress in chemotherapy and radiation
therapy has done little to increase the survival of patients with colon
cancer. This is why the genetic examination of HNPCC has become more popular.
However, developing diagnostics based on genetic information is a complicated
process because of the large number of mutations that have been identified
with HNPCC. Hopefully the results of the current genetic investigation
will provide a better understanding of the disease and the ability to treat
it more effectively.
|