Links:
HLA Gene
Studies of families in which more than one member with MS has indicated that the HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) class II region, located on chromosome 6, is involved in Multiple Sclerosis. "The HLA-DR2 haplotype (DRB1*1501 DQB1*0602) within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 6 is the strongest genetic effect identified in MS and has consistently demonstrated both linkage and assosiation in family and case control studies" (Baranzini 2002). The HLA patterns of individuals with MS are different from those without it. Studies previously done have shown a combination of three of the HLA genes, usually not seen in unafflicted individuals. Evidence from other studies show that different combinations of the HLAs may be linked to MS severity and progression.
The HLA consists of gene clusters that are linked on the short arm of chromosome 6 at 6p21.3 spanning 4 million base pairs. The HLA genes are highly polymorphic resulting in diverse genotypic combinations or haplotypes. Haplotypes DRB1*1501 and DQB1*0602 are correlated with MS. The molecular mechanism of DRB1*1501 may fail to negatively select or delete autoreactive T-cells. DQB1*0602 gene could encode class II recognition molecules that bind to peptide antigens of myelin and possibly stimulate encephalitogenic T-cells.
These alleles are always inherited together because they are in strong linkage disequilibrium. As a result of this, it is not known which allele is most responsible for MS susceptibility.
HLA DRB1*1501 (locus: 6p21.3 )
HLA-DRB1 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. The class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DRA) and a beta chain (DRB), both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa. It is encoded by 6 exons, exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DR molecule the beta chain contains all the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities. Hundreds of DRB1 alleles have been described and typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. DRB1 is expressed at a level five times higher than its paralogues DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. DRB1 is present in all individuals. Allelic variants of DRB1 are linked with either none or one of the genes DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. There are 4 related pseudogenes: DRB2, DRB6, DRB7, DRB8 and DRB9.
Click here to see a map of the gene
Click here to see the conserved domains
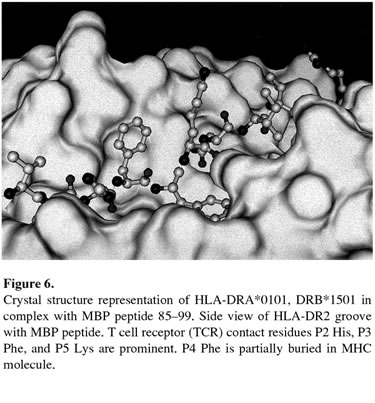
The DRB1*1501 allele is responsible for restricting the Myelin Basic Protien (MBP).
"Myelin basic protein (MBP) is a candidate autoantigen in MS because it can induce an MS-like disease, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, in rodents and primates with susceptible genetic backgrounds. The epitope MBP(85−99), which consists of amino acids 85−99 of MBP, is immunodominant in DR2-positive MS patients and binds to both DRB1*1501 and DRB5*0101 molecules, though in different registers. The disease relevance of the DRB1*1501-MBP(85−99) complex is supported by data showing that transgenic mice expressing the human DRB1*1501 molecule and an MS patient−derived TCR that recognizes the DRB1*1501-MBP(85−99) complex develop MS-like disease. In addition, an antibody that specifically recognizes the DRB1*1501-MBP(85−99) complex has been used to show that DRB1*1501-MBP(85−99) complexes are present in human MS lesions" (Lang et. al. 2002).
HLA DQB1*1602 (locus 6p21.3)
HLA-DQB1 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DQA) and a beta chain (DQB), both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and it contains 6 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DQ molecule both the alpha chain and the beta chain contain the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities, resulting in up to 4 different molecules. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow transplantation.
*information obtained from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=gene&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=Graphics&list_uids=3123